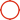
The load-bearing light steel frame can be used in multi-storey residential buildings with no more than 10 stories.
Construction form
In a multi-storey residential building, the walls are made of load-bearing lightweight steel panels, which are usually spaced at 600 mm centers. The floor is supported by the wall.
![]()
Load-bearing and supporting cross walls provide lateral stability, and these cross walls are usually also designed as partition walls for sound insulation and fire protection. The support can be a flat belt X support or an integral K support.
Application field
Multi-storey apartment, key worker residence, etc.
Technical details
The C-shaped cross-sections in wall panels are usually 100 mm deep and 1.5 to 2.0 mm thick, depending on their load (that is, it varies with the floor). At the lower level, C sections are usually placed in pairs; a single C-shaped section with reduced thickness is used in the upper part.
Two types of floor structures are commonly used:
- Light steel floor joist
- Laminate flooring.
![]()
In the first case, the depth of the floor joist is 200 to 250 mm and the span between the span walls is 4 to 6 m (for thicker sections, longer spans can be achieved). The dead weight of the suspended floor is usually 0.8 kN/m2, including the accumulation layer for sound insulation.
In the second case, the composite board has a depth of 150 to 200 mm, which can span similar distances, but its own weight is higher, ranging from 3.0 to 4.5 kN/m2. Longer spans may require support.
![]()
The main technical issues affecting the design of light steel frame mid- and high-rise residential buildings are:
- Stability under wind load
- Sound insulation material
- Fire performance.
Generally, two layers of 15 mm thick fire-resistant gypsum boards have mineral wool between the C section, which is enough to provide 90 minutes of fire resistance and high level of sound insulation for the light steel partition wall.